SAP SoD Matrix Template Excel: Free Download & Complete Guide
A Segregation of Duties (SoD) matrix is the foundation of access risk management in SAP. It defines which combinations of access rights create conflicts that could lead to fraud, errors, or compliance violations.
In this guide, you'll learn:
- What an SoD matrix is and why you need one
- How to structure your SAP SoD ruleset
- Best practices for maintenance
- How to automate SoD conflict detection
Plus, download our free SAP SoD matrix template to get started immediately.
What is a Segregation of Duties Matrix?
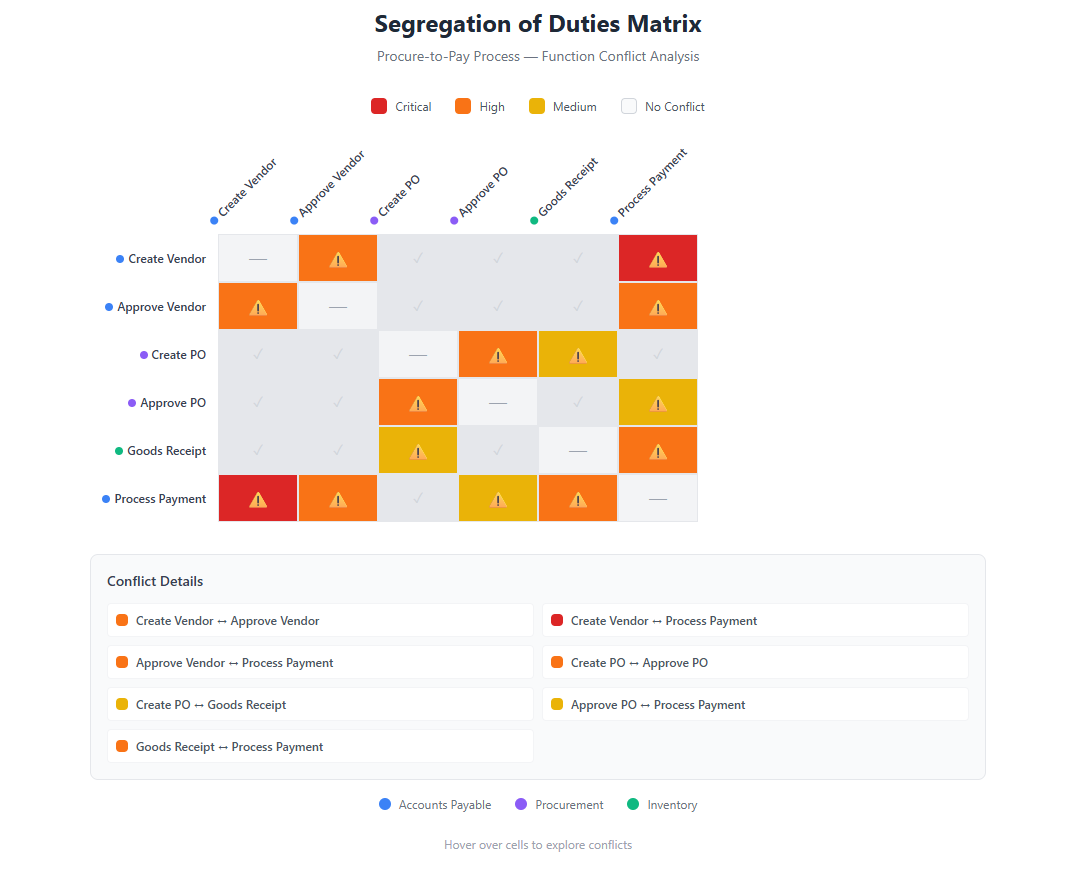
A Segregation of Duties matrix (also called an SoD ruleset or conflict matrix) is a document that defines incompatible access combinations within your organization. When a user has access to both sides of a conflict, they have the ability to perform actions that should require two separate people.
Example SoD Conflict
| Function A | Function B | Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Create Vendor | Process Payments | User could create fake vendor and pay themselves |
| Modify Inventory | Adjust GL Accounts | User could hide inventory theft |
| Create Purchase Order | Approve Purchase Order | User could approve their own purchases |
The matrix maps all such conflicts relevant to your business processes.
SAP SoD Matrix Structure
An effective SAP SoD matrix includes these components:
1. Risk Definition
Each risk in your matrix should have:
| Field | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Risk ID | Unique identifier | FI-001 |
| Risk Name | Short description | Vendor Master & Payment Processing |
| Risk Description | Detailed explanation | User can create vendors and process payments, enabling fraudulent payments |
| Business Process | Affected area | Finance, Procure-to-Pay |
| Risk Level | Critical/High/Medium/Low | Critical |
2. Function Definitions
Functions group related SAP transactions and authorization objects:
Function: Create Vendor Master
├── Transaction: XK01 (Create Vendor)
├── Transaction: XK02 (Change Vendor)
├── Transaction: FK01 (Create Vendor Accounting)
└── Auth Object: F_LFA1_BUK (Vendor Master Authorization)
3. Conflict Rules
The matrix then defines which function combinations create risks:
| Function A | Function B | Risk ID | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vendor Master Maintenance | Payment Processing | FI-001 | Critical |
| Purchase Order Creation | Purchase Order Approval | MM-001 | High |
| Goods Receipt | Invoice Verification | MM-002 | High |
Download: Free SAP SoD Matrix Excel Template
We've created a ready-to-use Excel (XLS) template that you can customize for your organization. This segregation of duties matrix template Excel file works as a starting point whether you manage SoD manually or plan to import it into an automated tool.
Download the Sample Template
Download SoD Matrix Sample (CSV) →
The sample includes:
- 8 example SoD risks (Finance, MM, SD, HR)
- 3 Critical Access rules
- Function definitions with SAP transaction codes
- Authorization object mappings
- Ready to import into MTC Skopos
Want a comprehensive ruleset with 400+ risks? Contact us for our full enterprise template.
How to Build Your SAP SoD Matrix
Step 1: Identify Critical Business Processes
Start with your highest-risk processes:
-
Procure-to-Pay (P2P)
- Vendor management
- Purchase orders
- Goods receipt
- Invoice processing
- Payments
-
Order-to-Cash (O2C)
- Customer management
- Sales orders
- Delivery
- Billing
- Collections
-
Financial Close
- Journal entries
- Account reconciliation
- Period close
- Financial reporting
-
Human Resources
- Employee master data
- Payroll processing
- Time management
Step 2: Define Functions
For each process, identify functions that should be separated:
Example: Procure-to-Pay Functions
| Function ID | Function Name | Key Transactions |
|---|---|---|
| P2P-01 | Vendor Master Maintenance | XK01, XK02, FK01, FK02 |
| P2P-02 | Purchase Requisition | ME51N, ME52N |
| P2P-03 | Purchase Order Creation | ME21N, ME22N |
| P2P-04 | Purchase Order Approval | ME28, ME29N |
| P2P-05 | Goods Receipt | MIGO, MB01 |
| P2P-06 | Invoice Verification | MIRO, MIR7 |
| P2P-07 | Payment Processing | F110, F-53, F-58 |
Step 3: Map Authorization Objects
Each action (transaction or Fiori app) should include the relevant SAP authorization objects:
Function: Payment Processing (P2P-07)
├── Action: F110 (Automatic Payment Program)
│ ├── F_REGU_BUK (Company Code) - FBTCH: 21, BUKRS: *
│ ├── F_REGU_KOA (Account Type) - FBTCH: 21, KOART: K
│ └── S_TCODE (Transaction) - TCD: F110
│
└── Action: F-53 (Post Vendor Payment)
├── F_BKPF_BUK (Company Code) - ACTVT: 01, BUKRS: *
├── F_BKPF_KOA (Account Type) - ACTVT: 01, KOART: K
└── S_TCODE (Transaction) - TCD: F-53
Step 4: Define Conflict Rules
Create rules that define which function combinations are incompatible:
| Rule ID | Function A | Function B | Risk Level | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P2P-R01 | Vendor Master (P2P-01) | Payment Processing (P2P-07) | Critical | Fraudulent vendor/payment creation |
| P2P-R02 | PO Creation (P2P-03) | PO Approval (P2P-04) | High | Self-approval of purchases |
| P2P-R03 | Goods Receipt (P2P-05) | Invoice Verification (P2P-06) | High | Fictitious receipt and invoice |
| P2P-R04 | PO Creation (P2P-03) | Goods Receipt (P2P-05) | Medium | Collusion opportunity |
Step 5: Assign Risk Ratings
Use a consistent rating framework:
| Rating | Definition | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Critical | Direct financial fraud risk, regulatory violation | Vendor + Payments, User Master + Payroll |
| High | Significant control bypass, material misstatement risk | PO Create + Approve, Journal Entry + Approve |
| Medium | Operational risk, policy violation | Duplicate function access, excessive access |
| Low | Minor control weakness, monitoring recommended | Display + limited change access |
SoD Matrix Best Practices
1. Start Focused, Expand Later
Don't try to cover everything at once:
- Begin with Critical and High risks
- Focus on your top 3 business processes
- Add Medium/Low risks over time
2. Involve Business Process Owners
Your IT or security team shouldn't define risks alone:
- Business owners understand which activities should be separated
- Finance should own financial SoD rules
- Compliance should validate against regulations
3. Consider Your Regulatory Requirements
Align your matrix with applicable regulations:
- SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley) - Financial reporting controls
- GDPR - Data access separation
- Industry-specific - Basel III (banking), FDA 21 CFR Part 11 (pharma)
4. Document Everything
Each risk should have:
- Clear business rationale
- Regulatory reference (if applicable)
- Remediation guidance
- Exception process
5. Review Annually (Minimum)
Your SoD matrix should evolve:
- New SAP transactions and objects
- Organizational changes
- Audit findings
- Regulatory updates
Common SAP SoD Risks by Module
Finance (FI)
| Risk | Function A | Function B |
|---|---|---|
| Vendor Fraud | Vendor Master Maintenance | Payment Execution |
| Journal Entry Fraud | Create Journal Entry | Post Journal Entry |
| Bank Master Fraud | Maintain Bank Master | Execute Payments |
| Asset Fraud | Create Asset | Post Asset Acquisition |
Materials Management (MM)
| Risk | Function A | Function B |
|---|---|---|
| Procurement Fraud | Create Purchase Order | Approve Purchase Order |
| Inventory Theft | Goods Receipt | Inventory Adjustment |
| Invoice Fraud | Goods Receipt | Invoice Verification |
| Vendor Kickbacks | Vendor Master | Purchase Order Creation |
Sales & Distribution (SD)
| Risk | Function A | Function B |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue Fraud | Create Sales Order | Create Billing Document |
| Customer Fraud | Customer Master | Credit Memo Processing |
| Pricing Fraud | Maintain Pricing | Create Sales Order |
Human Resources (HR)
| Risk | Function A | Function B |
|---|---|---|
| Payroll Fraud | Employee Master Maintenance | Payroll Processing |
| Ghost Employees | Create Employee | Payroll Execution |
| Time Fraud | Time Entry | Time Approval |
Automating SoD Analysis
Manually checking SoD conflicts against your matrix is:
- Time-consuming - Days or weeks for full analysis
- Error-prone - Easy to miss conflicts
- Point-in-time - Outdated immediately
The Solution: Automated SoD Analysis
Modern GRC tools automate the entire process:
- Import your ruleset - Use your Excel matrix
- Connect to SAP - Extract user/role data
- Run analysis - Detect all conflicts automatically
- Generate reports - Actionable remediation plans
MTC Skopos: Fast, Portable SoD Analysis
MTC Skopos is designed specifically for this:
- Import your Excel ruleset directly
- Connect to SAP via RFC or CSV import
- Analyze in minutes, not days
- Simulate changes before implementing
- Generate remediation plans automatically
See It In Action
No installation required. Upload your ruleset and run your first analysis today.
SoD Matrix Maintenance Checklist
Use this checklist to keep your matrix current:
Quarterly Review
- Review new SAP transactions released
- Check for organizational changes affecting access
- Validate risk ratings are still appropriate
- Update function definitions if needed
Annual Review
- Full matrix review with business owners
- Align with latest audit findings
- Update regulatory requirements
- Benchmark against industry standards
- Archive previous version for audit trail
Trigger-Based Updates
- New SAP module implementation
- Major organizational restructuring
- Regulatory changes
- Significant audit findings
- M&A activity
Frequently Asked Questions
How many risks should my SoD matrix have?
A typical enterprise SAP SoD matrix has 100-300 risks. Start with 50-100 critical/high risks and expand over time. Quality matters more than quantity.
Should I build my own matrix or use a pre-built template?
Both. Start with a pre-built template (like ours) as a foundation, then customize for your:
- Specific business processes
- Organizational structure (e.g. document types)
- Regulatory requirements
- Risk appetite
- Add customized Tcode/Apps/Auth
How often should I run SoD analysis?
- Continuous - For user provisioning (before granting access)
- Weekly/Monthly - For monitoring existing access
- Quarterly - For compliance reporting
- Annually - Full comprehensive review
What's the difference between SoD and Critical Access?
- SoD (Segregation of Duties) - Conflicts between two or more functions
- Critical Access - Single sensitive functions that require monitoring (e.g., Debug access, User administration)
Both should be included in your access risk management program.
Next Steps
- Download our SoD Matrix Sample - Get started with example risks
- Read: What is Segregation of Duties (SoD)? - Deep dive into SoD concepts and examples
- Try MTC Skopos Free - Import the sample and run your first analysis
Related Articles
- What is Segregation of Duties (SoD)? Meaning & Definition
- SoD Conflicts in SAP: How to Detect and Resolve Them - Practical conflict resolution guide
- Accounts Payable SoD Matrix: AP Segregation of Duties Guide - Industry-specific AP matrix
- Best SoD Tools & Software: Comparison Guide - Compare the leading SoD analysis solutions
- Advanced Remediation: Automated SAP Risk Resolution