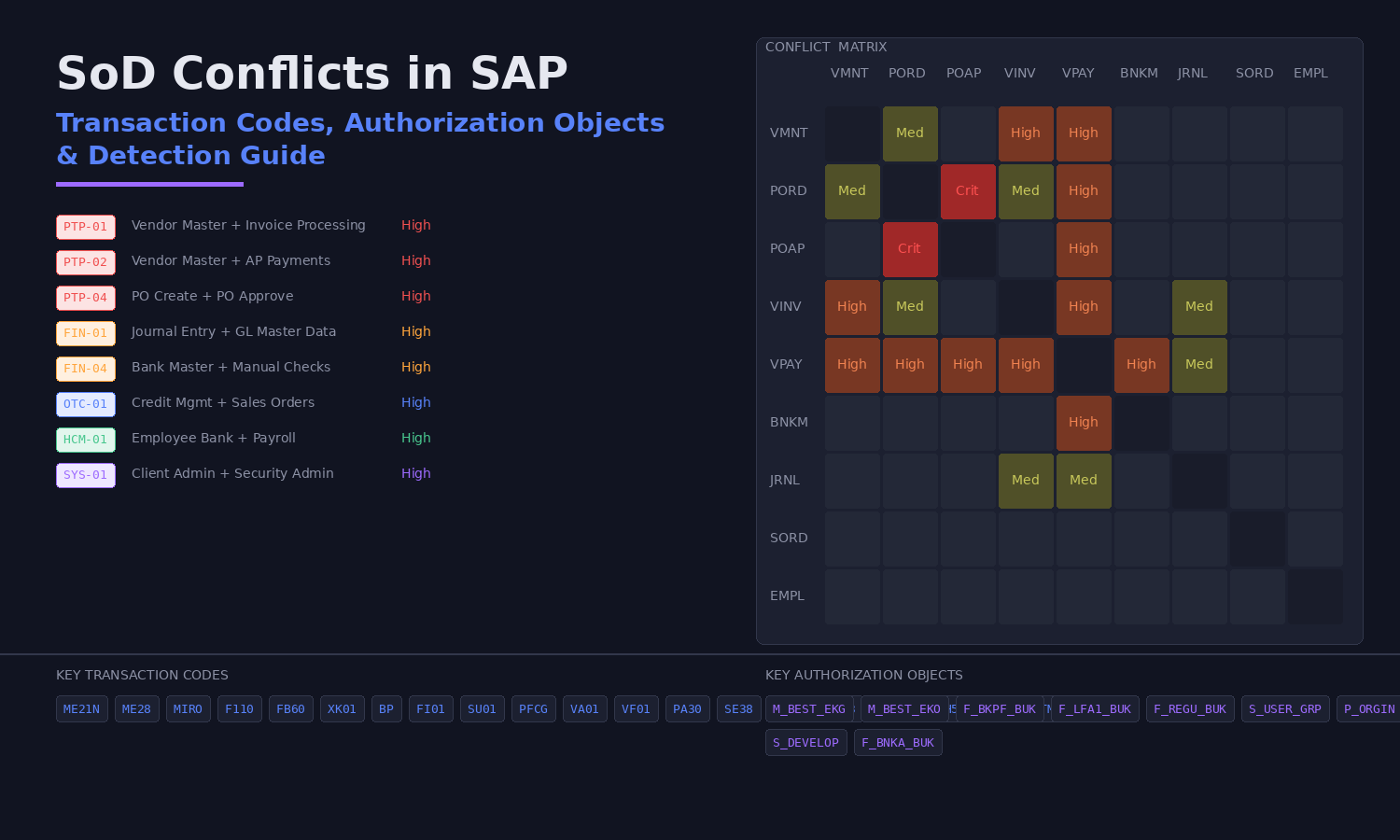
SoD Conflicts in SAP: Transaction Codes, Authorization Objects & Detection Guide
This article is a practical reference for identifying and detecting SoD conflicts in SAP. If you're looking for an introduction to what Segregation of Duties means and why it matters, start with our SoD fundamentals guide.
Here, we focus on the SAP-specific details: which transaction code combinations create conflicts, which authorization objects actually drive those conflicts, and how to run detection effectively.
SAP SoD conflict reference by module
The conflict examples below illustrate a typical production-grade SoD ruleset. A full SAP ruleset typically covers 300+ SoD risks and 50+ Critical Access risks across 180+ functions, thousands of classic transaction codes, and hundreds of Fiori apps - spanning procurement, finance, sales, HR/payroll, manufacturing, quality management, basis/security, and more. You can download a sample ruleset and import it directly into MTC Skopos.
Procure-to-pay (P2P) - 82 SoD risks
The P2P process contains the highest volume of SoD risks in SAP, with 82 risks (32 High) covering purchasing, receiving, invoicing, and payment functions.
PTP-01 - Vendor Master Maintenance & Invoice Processing (High)
A user who can maintain vendor records AND process invoices could create a fictitious vendor and submit invoices for payment.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Fiori Apps | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|---|
| VMNT - Vendor Master | BP, FK01, FK02, FK05, FK06, MK01, MK02, XK01, XK02, XK05 | F0593, F0871, F1546, F3336 | F_LFA1_BUK, F_LFA1_APP, F_LFA1_GEN, B_BUPA_RLT |
| VINV - Invoice Processing | F-02, F-04, F-43, F-44, MIRO, MIR4, MIR7, FB60, FV60 | F0859, F0717A, F1339 | F_BKPF_BUK, F_BKPF_KOA, M_RECH_BUK |
PTP-02 - Vendor Master & AP Payments (High)
A user could create a ghost vendor or change bank account details and direct payments to themselves.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Fiori Apps | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|---|
| VMNT - Vendor Master | BP, FK01, FK02, FK05, XK01, XK02 | F0593, F0871, F1546 | F_LFA1_BUK, F_LFA1_APP, B_BUPA_RLT |
| VPAY - AP Payments | F-53, F-58, F110, F-04, F-51, F-52 | BNK_APP | F_REGU_BUK, F_REGU_KOA, F_PAYR_BUK |
PTP-03 - Invoice Processing & AP Payments (High)
A user could create a fraudulent invoice and process the payment, particularly risky when alternative payee is available.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|
| VPAY - AP Payments | F-04, F-06, F-07, F-18, F-51, F-52, F-53, F-58, F110 | F_REGU_BUK, F_REGU_KOA, F_PAYR_BUK, F_AVIK_BUK |
| VINV - Invoice Processing | F-02, F-43, F-44, MIRO, MIR4, MIR7, FB60, FV60 | F_BKPF_BUK, F_BKPF_KOA, M_RECH_BUK |
PTP-04 - Purchase Order Create & Approve (High)
A user could raise and approve their own purchase order, bypassing approval workflows.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Fiori Apps | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|---|
| PORD - Purchase Orders | ME21N, ME22N, ME23N, ME51N, ME52N | F0547B, F0752, F0842, F1702, F1982 | M_BEST_EKG, M_BEST_EKO, M_BEST_WRK, M_BANF_EKG |
| POAP - PO Approval | ME28, ME29N, ME35 | M_BEST_EKG, M_BEST_EKO, M_BEST_WRK, M_EINK_FRG |
PTP-05 - Purchase Order & Invoice Processing (Medium)
A user could purchase items and process the invoice, resulting in unauthorized payments.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Fiori Apps | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|---|
| PORD - Purchase Orders | ME21N, ME22N, ME23N, ME28, ME29N, ME51N, ME52N | F0547B, F0752, F0842, F1702, F1982 | M_BEST_EKG, M_BEST_EKO, M_BEST_WRK, M_BANF_EKG, M_BANF_EKO |
| VINV - Invoice Processing | F-02, F-43, F-44, MIRO, MIR4, MIR7 | F0859 | F_BKPF_BUK, F_BKPF_KOA, M_RECH_BUK |
Other High-Risk P2P conflicts commonly found in production rulesets include: PTP-06 (PO + Payment), PTP-07 (PO + Vendor Master), PTP-08 (PO + Blocked Invoice Release), PTP-09 (Goods Receipt + Inventory Count), PTP-10 (Material Master + PO), PTP-11 (Invoice + Bank Reconciliation), PTP-12 (Payment + Bank Reconciliation), PTP-13 (Manual Check + Vendor Master), PTP-04 (PO Create + Approve), PTP-14 (Vendor Account + Bank Reconciliation), PTP-15 (Invoice + Vendor Bank Account + EFT), and PTP-16 (PO + Cost Center).
Financial accounting (FI) - 49 SoD risks
The FI module covers 49 risks (21 High) spanning general ledger, asset accounting, bank master data, cost accounting, project systems, and treasury.
FIN-01 - Journal Entry & GL Master Data (High)
A user who can create GL accounts and post journal entries could set up incorrect accounts and misstate financial statements.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Fiori Apps | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|---|
| JRNL - Post Journal Entry | F-02, F-03, F-04, FB01, FB50, FB60 | F0717, F0718, F1119, F1240 | F_BKPF_BUK, F_BKPF_KOA, F_SKA1_BUK |
| GLMD - GL Master Data | FS00, FSP0, FSS0, EK71, EK72 | F_SKA1_BUK, F_SKA1_KTP |
FIN-02 - Bank Master & AP Payments (High)
A user could create a fictitious bank account and route vendor payments to it.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|
| BNKM - Bank Master Data | FI01, FI02, FI12, BAUP, F9K1, FIBAN | F_BNKA_BUK, F_BNKA_MAN, F_CLM_BAM, F_PMT_TRNS |
| VPAY - AP Payments | F-53, F-58, F110, F-51, F-52 | F_REGU_BUK, F_REGU_KOA, F_PAYR_BUK |
FIN-03 - Asset Master & Asset Documents (High)
A user could create asset records and process acquisitions, retirements, or depreciation, enabling write-offs and misappropriation.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Fiori Apps | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMST - Asset Master | AS01, AS02, AS05, AS11, AS21 | F1592, F3425 | A_S_ANLGR, A_S_ANLKL, F_BKPF_BUK |
| ADOC - Asset Documents | AB01, ABAA, ABAD, ABAV, ABAW, ABAON | A_B_ANLKL, A_B_BWART, F_BKPF_BUK |
FIN-04 - Bank Master & Manual Check Processing (High)
A user could create a fictitious bank account and process manual checks to divert payments.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|
| BNKM - Bank Master Data | FI01, FI02, FI12, BAUP, F9K1, F9K2, FIBAN | F_BNKA_BUK, F_BNKA_MAN, F_CLM_BAM, F_PMT_TRNS |
| MCHK - Manual Check | FCH3, FCH4, FCH5, FCH6, FCH7, FCHE, FCHF, FBZ5 | F_REGU_BUK, F_REGU_KOA, F_PAYR_BUK, F_BKKA_BKA |
Other High-Risk FI conflicts include: FIN-05 (Cost Center + Cost Transfer), FIN-06 (Cash Application + Bank Reconciliation), FIN-07 (Asset Master + Goods Receipt), FIN-08–FIN-10 (Project Settlement + Overhead), FIN-11 (Bank Master + Customer Payment), FIN-12 (Treasury Create + Confirm), FIN-13 (Bank Master + AR Payments), FIN-14 (Vendor Invoice + Cost Center), FIN-15 (Bank Master + Treasury), FIN-16 (Vendor Invoice + Asset Master), FIN-17 (Cash Application + Treasury), and FIN-18–FIN-19 (Treasury risks).
Accounts receivable & sales (SD) - 46 SoD risks
The SD module covers 46 risks (23 High) spanning customer master, sales orders, billing, credit management, rebates, and cash application.
OTC-01 - Credit Management & Sales Order Processing (High)
A user who controls credit limits and processes sales orders could exceed credit limits to process unauthorized transactions.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Fiori Apps | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|---|
| CRDT - Credit Management | FD32, FD37, UKM_BP, BP | F3163, F3748, F4596 | F_KNKA_KKB, F_KNKA_MAN, B_BUPA_RLT |
| SORD - Sales Orders | VA01, VA02, VA03, VL01N, VL02N, VF01, VF02 | F1119, F1240, F1478, F1510 | V_KNKK_FRE, V_KONH_VKS, V_VBAK_AAT |
OTC-02 - Customer Master & Sales Rebates (High)
A user maintaining customer data and controlling rebate processing could set up fraudulent rebate agreements.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Fiori Apps | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|---|
| CMNT - Customer Master | BP, FD01, FD02, FD05, FD06, XD01, XD02, VD01, VD02 | F0593, F0871, F1546, F3336 | F_KNA1_BUK, F_KNA1_APP, B_BUPA_RLT |
| SREB - Sales Rebates | VB(6, VB(7, VBN1, VBN2, VBO1, VBO2, VBOF, WAK1 | F2954 | V_KONA_VKO, V_VBAK_VKO, V_VBRK_VKO |
OTC-03 - Sales Order & Credit Memo Processing (High)
A user could create a sales order, obtain goods, and process a credit memo to reverse the balance.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Fiori Apps | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|---|
| SORD - Sales Orders | VA01, VA02, VL01N, VL02N, VF01, VF02 | F1119, F1240, F1478, F1510, F1814, F4572 | V_KNKK_FRE, V_KONH_VKS, I_TCODE |
| CRMM - Credit Memos | F-02, F-21, F-27, F-43, FB01, FB50 | F3068, F5281 | F_BKPF_BUK, F_BKPF_KOA |
Other High-Risk SD conflicts include: OTC-04 (Sales Order + Clear Customer), OTC-05 (Invoice + Clear Customer), OTC-06–OTC-07 (Pricing + Sales/Invoice), OTC-08 (Cash + Customer Master + Contracts), OTC-09 (Sales Order + Release Block), OTC-10 (Credit Limit + Invoice), OTC-11 (Customer Master + Clear Balance), OTC-12 (Customer Master + Billing), OTC-13–OTC-14 (Sales Order + Credit Memo), OTC-15 (Invoice + Clear Customer), OTC-16–OTC-17 (Customer Master + Credit), and OTC-18–OTC-19 (Payment/Pricing/Billing combinations).
HR / Payroll - 31 SoD risks
The HR module covers 31 risks (12 High) across employee master data, payroll processing, time management, and personnel development.
HCM-01 - Employee Bank Account & Payroll Processing (High)
An employee could change another employee's bank account details and process payroll, diverting payments.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Fiori Apps | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|---|
| EMPL - Employee Master Data | PA30, PA42, PA70, PA10 | F2288 | P_ORGIN, P_TCODE |
| PYRL - Process Payroll | PA03, PA04, PC00_M*_CALC | F0691 | P_ORGIN, P_PYEVRUN, F_REGU_BUK |
HCM-02 - Time Entry & Time Approval (High)
A user could enter and approve timesheets, enabling fraudulent payroll payments.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Fiori Apps | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|---|
| TIME - Time Data | CAT2, CAT4, CAT6, CAPP, CAPS | F0409B, F1312, F1506 | P_ORGIN, P_ORGXX |
| TAPP - Approve Time | CATS_APPR, CATS_APPR_LITE, CAT4 | F1314, F2585 | P_ORGIN |
HCM-03 - Employee Bank Account & Position Maintenance (High)
A user could alter an employee's position to a higher pay rate and change their bank account to intercept payments.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|
| EMPL - Employee Master Data | PA30, PA42, PA70 | P_ORGIN, P_TCODE |
| PDST - PD Structure | PA48, PFOM, PFTC, OOOE, OOOU | PLOG, P_ORGIN |
Other High-Risk HR conflicts include: HCM-04 (Timesheet + Position), HCM-05 (Employee Master + Time Data), HCM-06 (Payroll Status + Bank Account), HCM-07 (Payroll Status + Payments), HCM-08 (Write Lock + Unlock Records), HCM-09 (Position + Payroll), HCM-10 (Payment Amount + Bank Account), HCM-11 (Payment Amount + Payroll Config), and HCM-12 (Bank Account + Payroll Config).
Manufacturing & materials (MM) - 17 SoD risks
The MM module covers 17 risks (6 High) focused on goods movements, inventory management, and warehouse management.
INV-01 - Goods Receipt/Issue & Inventory Count (High)
A user could receive or issue incorrect quantities and adjust the stock count to hide the discrepancy.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Fiori Apps | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|---|
| GMOV - Goods Movements | MIGO, MB01, MB1A, MB1B, MB1C | M_MSEG_BWA, M_MSEG_WWA, M_MATE_WRK | |
| ICNT - IM Counts | MI01, MI02, MI04, MI05 | F1512, F3197, F3340 | M_ISEG_WDB, M_ISEG_WIB |
| ICLR - IM Clear Differences | MI07, MI08, MI10, MI35, MI37 | M_ISEG_WZB, M_ISEG_WZL |
INV-02 - Goods Movements & WM Inventory Count/Adjust (High)
A user who moves goods and controls warehouse inventory counts could misappropriate goods and adjust counts to cover the discrepancy.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|
| GMOV - Goods Movements | MIGO, MB01, MB1A, MB1B | M_MSEG_BWA, M_MATE_WRK |
| WCNT - WM Counts | LI01, LI02, LI06, LI11, LI12 | /SCWM/PIPR, C_LIME_SI |
| WCLR - WM Clear Differences | LI20, LI21, LQ02, LT02 | /SCWM/PIPR, M_MSEG_BWA |
Other High-Risk MM conflicts include: INV-03 (Quality Results + WM Count/Clear), INV-04 (Journal Entry + WM Count/Clear), INV-05 (Goods Movements + IM Count/Clear), and INV-06 (Journal Entry + IM Count/Clear).
SAP Basis / Security - 27 SoD risks
The Basis module covers 27 risks focused on development, configuration, transport management, security administration, and client administration.
SYS-01 - Client Administration & Security Administration (High)
A user with client admin and security admin access could modify security parameters and replicate changes across the landscape.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|
| CLAD - Client Admin | SCC4, SCCL, SCC1, SCC9, FOD0, FOD1 | S_CLNT_IMP, S_TABU_CLI, S_ADMI_FCD |
| SCAD - Security Admin | SU01, SU10, SU24, PFCG, SU25 | S_USER_GRP, S_USER_AGR, S_USER_AUT |
SYS-02 - Create Transport & Perform Transport (High)
A user who can both create and execute transports bypasses the dual-control principle of change management.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|
| CTRS - Create Transport | SE01, SE09, SE10, STMS | S_CTS_ADMI, S_TRANSPRT |
| PTRS - Perform Transport | STMS, SCC1 | S_CTS_ADMI, S_TRANSPRT |
SYS-03 - User Maintenance & Role/Profile Maintenance (High)
A user who can both maintain users and maintain roles could assign inappropriate authorizations to themselves.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|
| USRM - User Master | SU01, SU10 | S_USER_GRP, S_USER_AUT |
| ROLM - Roles/Profiles | PFCG, SU24, SU25 | S_USER_AGR |
SYS-04 - Development & System Administration (Medium)
A developer with system admin access could deploy changes without proper oversight.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|
| DEVL - Development | SE38, SE80, SE24, SE37, CMOD, DMWB, SMOD | S_DEVELOP, S_PROGRAM, S_TABU_DIS |
| SYAD - System Admin | SM21, SM37, SM50, SM51, SM66, STMS, SE09, SE10 | S_ADMI_FCD, S_BDC_MONI, S_BTCH_ADM |
SYS-05 - Development & Configuration (Medium)
A developer who can also change configuration could introduce changes that bypass standard change management.
| Function | Key Transactions | Key Fiori Apps | Key Auth Objects |
|---|---|---|---|
| DEVL - Development | SE38, SE80, SE24, SE37, CMOD | S_DEVELOP, S_PROGRAM | |
| CNFG - Configuration | SPRO, SM30, SM31, SM34 | F1273, F2190, F2273 | S_TABU_DIS, S_TABU_NAM, S_RZL_ADM |
Other Basis risks include: SYS-06 (Development + Client Admin), SYS-07 (Development + Transport), SYS-08–SYS-11 (Utilities + System/Config/Client/Transport), SYS-12–SYS-13 (Table Maintenance + System/Client), SYS-14 (Security + Transport), SYS-15 (Configuration + Transport), and SYS-16 (Client Admin + Configuration).
Additional modules
A full SoD ruleset also covers:
- Quality Management (QM) — 10 risks covering inspection plans, results recording, usage decisions, and quality notifications
- Plant Maintenance (PM) — 7 risks covering work orders, bill of materials, equipment maintenance, and cost settlement
- Consolidation (EC/G) — 16 risks covering consolidation data models, eliminations, and journal processing
- Joint Venture (JV) — 9 risks covering JVA master data, billing, invoicing, and payments
- BPC (BP) — 25 risks covering planning, consolidation journals, security, and data management
- Environment Health & Safety (EH) — 1 risk covering dangerous goods management
Key SAP authorization objects for SoD
Transaction codes alone don't tell the full story. Two users might both have access to ME21N (Create Purchase Order), but their actual authority differs based on authorization objects. Effective SoD analysis must check at the authorization object level to avoid false positives.
A well-designed ruleset references hundreds of authorization objects. Here are the most important ones by area:
Procurement objects
| Object | Name | Fields | SoD Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| M_BEST_EKG | PO - Purchasing Group | ACTVT, EKGRP | Scopes PO create/change by purchasing group. A conflict is only real if EKGRP values overlap across both functions. |
| M_BEST_EKO | PO - Purchasing Org | ACTVT, EKORG | Controls purchasing at the org level. Critical for cross-company SoD analysis. |
| M_BEST_WRK | PO - Plant | ACTVT, WERKS | Plant-level purchasing scope. A user creating POs in Plant 1000 and approving in Plant 2000 may not have a real conflict. |
| M_BANF_EKG | Requisition - Purch. Group | ACTVT, EKGRP | Scopes purchase requisition processing. Key for requisition-to-PO conflicts. |
| M_BANF_BSA | Requisition - Doc Type | ACTVT, BSART | Controls which requisition document types a user can process. |
| M_RECH_BUK | Invoice Verification - CoCd | ACTVT, BUKRS | Controls invoice processing by company code. Key for the GR + invoice and invoice + payment conflicts. |
Finance objects
| Object | Name | Fields | SoD Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| F_BKPF_BUK | Accounting Doc - CoCd | ACTVT, BUKRS | The most referenced FI object. Controls financial document creation/change by company code. |
| F_BKPF_KOA | Accounting Doc - Acct Type | ACTVT, KOART | Determines which account types (K=Vendor, D=Customer, S=GL, A=Asset) a user can post to. |
| F_LFA1_BUK | Vendor Master - CoCd | ACTVT, BUKRS | Controls vendor master maintenance. Central to the vendor + payment conflict. |
| F_REGU_BUK | Auto Payment - CoCd | FBTCH, BUKRS | Controls access to the automatic payment program (F110). |
| F_REGU_KOA | Auto Payment - Acct Type | FBTCH, KOART | Further restricts payment access by account type. |
| F_BNKA_BUK | Bank Master - CoCd | ACTVT, BUKRS | Controls bank master record maintenance. Key for the bank + payment conflict. |
| F_PAYR_BUK | Payment Run - CoCd | ACTVT, BUKRS | Controls payment document access. |
HR / Payroll objects
| Object | Name | Fields | SoD Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| P_ORGIN | HR Master Data | INFTY, SUBTY, AUTHC, PERSA, PERSG, VDSK1 | Controls access to employee master data by infotype, personnel area, and authorization level. The most critical HR object. |
| P_ORGXX | HR Master Data (Extended) | INFTY, SUBTY, AUTHC + org fields | Extended version with additional organizational checks. |
| P_PYEVRUN | Payroll Run | PYEVTYPE, PYEVRUN | Controls which payroll runs a user can execute. Key for payroll processing conflicts. |
| PLOG | Personnel Planning | INFOTYP, SUBTYP, PLVAR | Controls PD (position/organizational) master data. |
Basis / Security objects
| Object | Name | Fields | SoD Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| S_USER_GRP | User Maintenance - Group | ACTVT, CLASS | Controls user administration by user group. |
| S_USER_AGR | Role Assignment | ACTVT, ACT_GROUP | Controls who can assign roles to users. |
| S_DEVELOP | Development | DEVCLASS, OBJTYPE, ACTVT | Controls ABAP development access. ACTVT=02 (change) with debug capability is a critical access risk. |
| S_TABU_DIS | Table Maintenance - Auth Group | ACTVT, DICBERCLS | Controls access to table maintenance (SM30/SM31). Wide-open S_TABU_DIS is a common audit finding. |
| S_ADMI_FCD | System Admin Functions | S_ADMI_FCD | Controls access to administrative functions like client copy and system-level operations. |
| S_TRANSPRT | Transport | TTYPE, ACTVT | Controls transport creation and execution. Key for the create + perform transport conflict. |
Why authorization-level analysis matters
Transaction-level SoD analysis flags every user with access to both XK01 and F110 as having a conflict. Authorization-level analysis checks whether the user's F_LFA1_BUK company code values overlap with their F_REGU_BUK values. If a user can only maintain vendors in company code 1000 but only run payments in company code 2000, there is no real conflict.
A production ruleset references hundreds of authorization objects across all SoD risks, each constraining the scope of what a user can actually do. Without checking these values, SoD analysis generates excessive false positives.
MTC Skopos performs this deep authorization analysis automatically, producing precise results that focus your remediation efforts where they matter.
How to detect SoD conflicts in SAP
Method 1: Manual analysis via SUIM
SAP provides built-in reports through transaction SUIM (User Information System):
- Extract user-role assignments: SUIM → Roles → By User Assignment
- Extract role-transaction mappings: SUIM → Roles → By Transaction
- Export to Excel and cross-reference against your SoD ruleset
Limitations:
- Time-consuming (days for large environments)
- Doesn't check authorization object values
- Point-in-time snapshot, outdated immediately
- Error-prone manual cross-referencing
- No automated remediation guidance
Method 2: SAP GRC Access Control (ARA)
SAP's Access Risk Analysis module provides automated detection:
- Configure your SoD ruleset in the GRC system
- Schedule or run ad-hoc risk analysis
- Review results in the GRC dashboard
Limitations:
- Requires dedicated infrastructure (servers, database)
- Implementation takes weeks to months
- Per-user pricing that scales with landscape size
- Analysis can take hours for large user populations
- Basic remediation suggestions
Method 3: MTC Skopos (recommended)
MTC Skopos provides fast, deep SoD conflict detection:
- Import data: Connect via SAP RFC or import CSV exports
- Load ruleset: Import your SoD ruleset from Excel — MTC Skopos supports any custom ruleset, and our consulting team can build one tailored to your landscape
- Run analysis: Full system analysis completes in minutes
- Review results: Conflicts shown with specific users, roles, transactions, and authorization values
- Get remediation: Advanced algorithm provides step-by-step resolution plans
Advantages:
- Authorization-level analysis (fewer false positives)
- Minutes, not hours
- No infrastructure requirements
- Did-do analysis distinguishes theoretical vs. actual risk
- Advanced Remediation provides specific fix steps
- Data never leaves your infrastructure
SoD conflicts in S/4HANA
S/4HANA introduces new authorization layers that expand the conflict surface. A modern ruleset must cover both traditional transaction codes and their Fiori equivalents, including hundreds of Fiori apps alongside thousands of classic transactions:
Fiori app coverage in a modern ruleset
The ruleset maps Fiori apps to the same functions as their classic transaction equivalents. For example:
| Function | Classic Transactions | Fiori Apps |
|---|---|---|
| VMNT - Vendor Master | XK01, FK01, BP | F0593, F0871, F1546, F3336 |
| PORD - Purchase Orders | ME21N, ME22N, ME51N | F0547B, F0752, F0842, F1702, F1982 |
| JRNL - Journal Entry | FB01, FB50, F-02 | F0717, F0718, F1119, F1240 |
| SORD - Sales Orders | VA01, VL01N, VF01 | F1119, F1240, F1478, F1510, F1814 |
| TIME - Time Data | CAT2, CAT4, CAPP | F0409B, F1312, F1506 |
| CNFG - Configuration | SPRO, SM30 | F1273, F2190, F2273, F2704 |
A ruleset that only checks classic transaction codes would miss users who access these functions exclusively through Fiori apps.
OData services and authorization
Fiori apps use OData services like MM_PUR_PO_MAINT_V2_SRV which require:
- S_SERVICE (OData service authorization)
- S_START (App start authorization)
- Traditional M_BEST_* objects for business logic
New authorization patterns
- Business roles (BR_*) aggregate multiple business catalogs
- Business catalogs (SAP_*) group Fiori apps and services
- Spaces and pages control Fiori Launchpad layout but not authorization
A user might have no access to ME21N but full access to the "Manage Purchase Orders" Fiori app. A ruleset that only checks transaction codes would miss this.
Frequently asked questions
How do you check SoD conflicts in SAP?
You can check SoD conflicts in SAP using dedicated SoD analysis tools like MTC Skopos or SAP GRC Access Control, or by extracting user roles via SUIM and cross-referencing against an SoD ruleset. Automated tools compare user access at the authorization object level and flag all conflicts within minutes.
What SAP authorization objects are important for SoD?
Key SAP authorization objects for SoD analysis include M_BEST_EKG (purchasing group), M_BEST_EKO (purchasing organization), M_BEST_WRK (plant), F_BKPF_BUK (company code for financial postings), F_LFA1_BUK (vendor master), and F_REGU_BUK (automatic payments). These objects define the actual scope of user access beyond transaction codes.
What is the difference between transaction-level and authorization-level SoD analysis?
Transaction-level analysis only checks which transaction codes a user can execute. Authorization-level analysis also checks the authorization object values (company code, purchasing group, plant, etc.) to determine whether the user's access actually overlaps across conflicting functions. Authorization-level analysis produces fewer false positives.
Related articles
- What is Segregation of Duties (SoD)? Meaning & Definition - SoD fundamentals and concepts
- SAP SoD Matrix Template: Free Excel Download - Build your SoD ruleset
- Accounts Payable SoD Matrix - AP-specific conflict reference
- Best SoD Tools & Software Comparison - Compare detection solutions
- Building an Effective SoD Ruleset for S/4HANA - S/4HANA-specific guidance
- Advanced Remediation: Automated SAP Risk Resolution - How to fix conflicts
- Did-Do Analysis: Real Risks, Not Theoretical - Distinguish conflicts from violations
Ready to detect your SAP SoD conflicts? Explore MTC Skopos features or contact us for a demonstration.